
Neuroglial Cells
Overlaid cells in t-SNE plots with marker genes for SGC and Schwann cells show the relative levels of expression as a color. neuroglial cells and number and volume of nerve cells in the spinal.

Medical Terms & Сlinical Сases Neuron
. The neon green structures in the picture are . The neuron is one of two basic types of cells in the nervous system. The other type is the neuroglial cell. Neurons — also called nerve cells — are electrically excitable cells that are the main functional units of the nervous system . Their function is to transmit nerve impulses

Color the Neuron and Neuroglial Cells Answer Key CameronkruwMccann
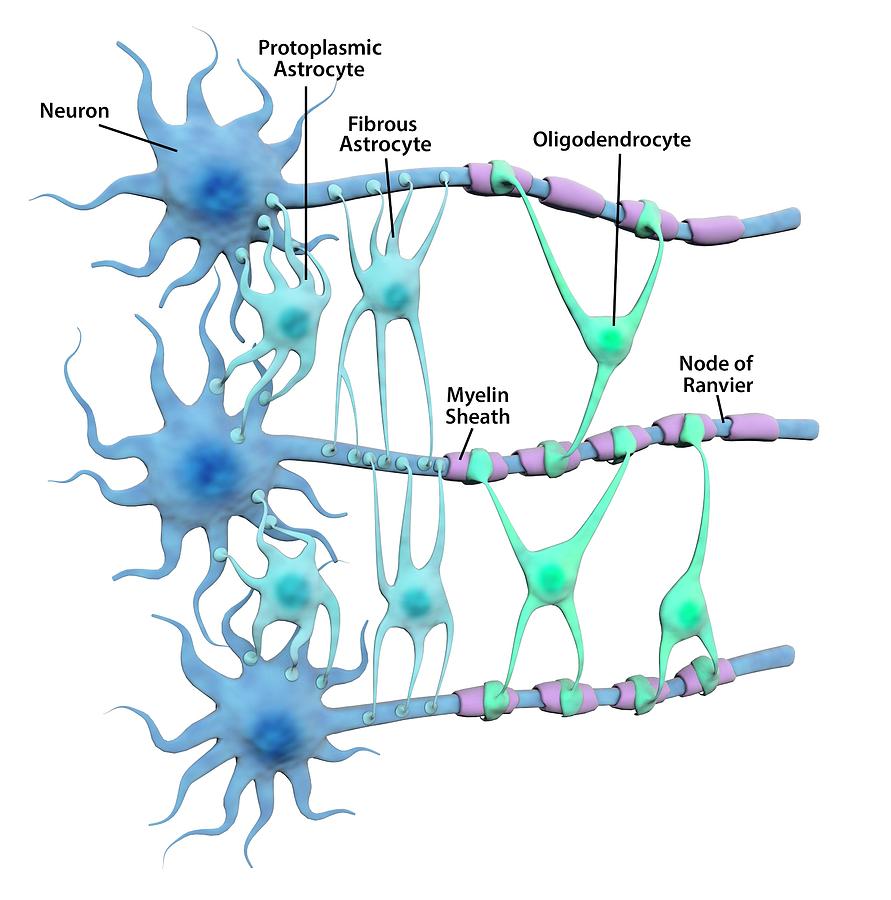
astrocyte: a neuroglial cell, in the shape of a star, in the brain. Neurogila or glial cells, are non-neuronal cells that maintain homeostasis, form myelin, and provide support and protection for neurons in the central (CNS) and peripheral nervous systems (PNS). It was long believed that neuroglia did not play any role in neuro-transmission.
19+ Art Labeling Activity Neuroglial Cells Of The Cns MarilyamShae
The neuron is one of two basic types of cells in the nervous system, the other type being the glial cell. Figure 11.3.1 11.3. 1: Interneurons of Adult Visual Cortex. Neurons, also called nerve cells, are electrically excitable cells that are the main functional units of the nervous system. Their function is to transmit nerve impulses.

Color The Neuron And Neuroglial Cells
2) Describe the path of a nerve impulse in a neuron starting with the dendrite: Color the Neuron and Neuroglial Cells is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts.

Neuron and Neuroglial Cells 8131534 Vector Art at Vecteezy
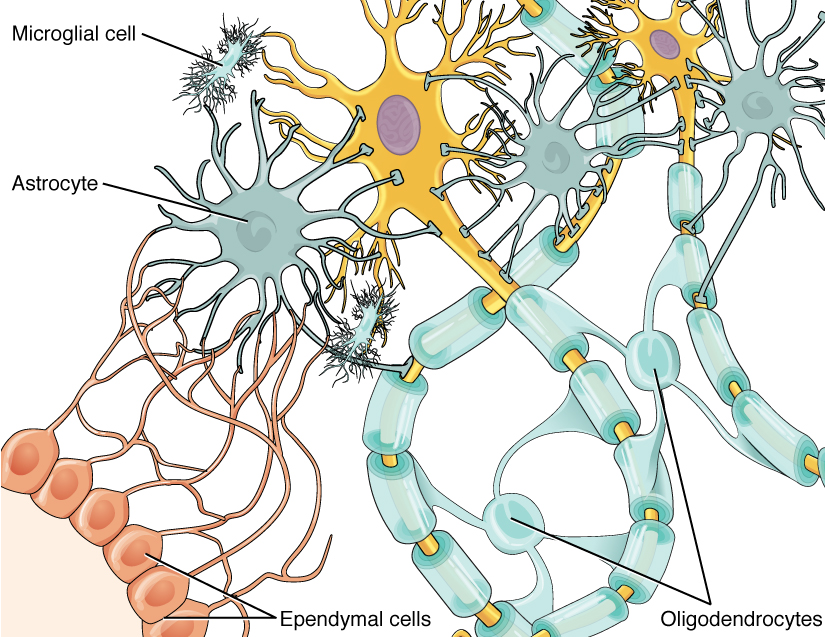
Figure 35.3.1 35.3. 1: Glial cells: Glial cells support neurons and maintain their environment. Glial cells of the (a) central nervous system include oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells, and microglial cells. Oligodendrocytes form the myelin sheath around axons. Astrocytes provide nutrients to neurons, maintain their extracellular.

Color The Neuron And Neuroglial Cells
Like the heart, lungs, and stomach, the nervous system is made up of specialized cells. These include nerve cells (or neurons) and glial cells (or glia ). Neurons are the basic functional units of the nervous system, and they generate electrical signals called action potentials, which allow them to quickly transmit information over long distances.

Color The Neuron And Neuroglial Cells
Neuroglia cells are different from nerve cells in that they do not participate directly in synaptic interactions Students can also label a nerve cell and color neuroglia cells using paper handouts. I have also had students model neurons with clay and chalk markers.

Color The Neuron And Neuroglial Cells
For each of the cells above, color the nucleus a darker shade of purple, green, blue, orange Myelin sheaths (pink) Capillary (red) Microglial cells (yellow) Nodes or Ranvier and the Axon (brown) What is the function of: 1) Oligodendrocytes _______ make the myelin sheaths ______________________________
Brain Neurons And Neuroglia Photograph by Gunilla Elam/science Photo
1.1. The Birth of the Concept of Homoeostatic Neuroglia. The complexity of the human brain is remarkable: a population of more than 200 billion (i.e. 2 × 10 11) neural cells (neurones and neuroglia) is packed within a limited volume (average human brain occupies 1200-1400 cm 3).These neural cells form complex networks, connected through 15-20 trillions of chemical and electrical synapses.

Nervous Tissue Mediates Perception and Response Anatomy and Physiology I
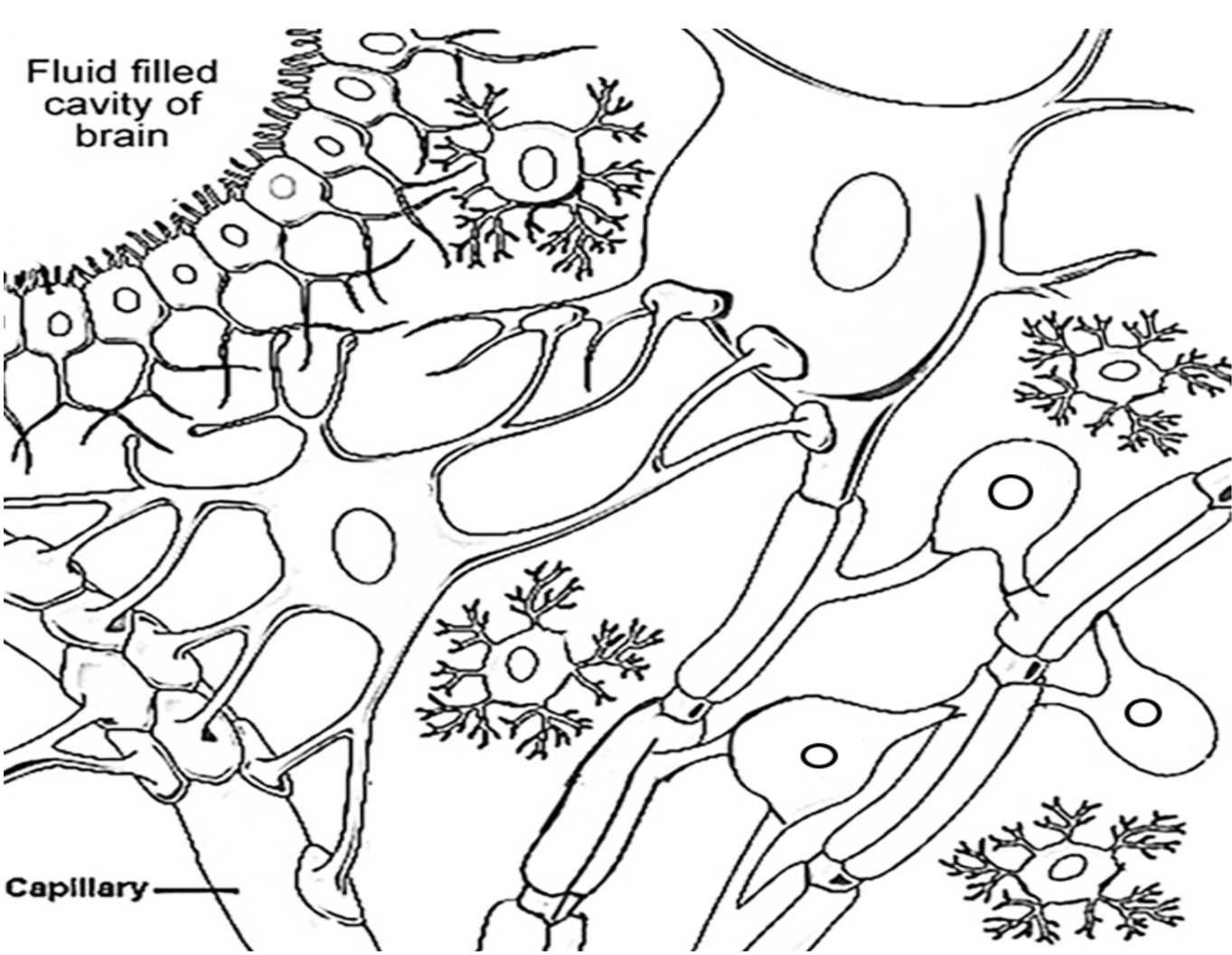
Figure 1.4 Neuroglial cells. Tracings of an astrocyte (A), an oligodendrocyte (B), and a microglial cell (C) visualized by impregnation with silver salts. The images are at approximately the same scale. (D) Astrocytes in the brain labeled with an antibody against (more.)
Histology of the Peripheral Nerves and Light Microscopy NYSORA
Today, we recognize three broad groups of glial cells: (i) true glial cells or macroglia, such as astrocytes and oligodendrocytes, of ectodermal origin, the stem cell of which is the spongioblast; (ii) microglia, of mesodermal origin; and (iii) ependymal cells, also of ectodermal origin and sharing the same stem cell as true glia.

Neurons Neuroglial Cells Glial Cells Nonneuronal Stock Vector 235015666
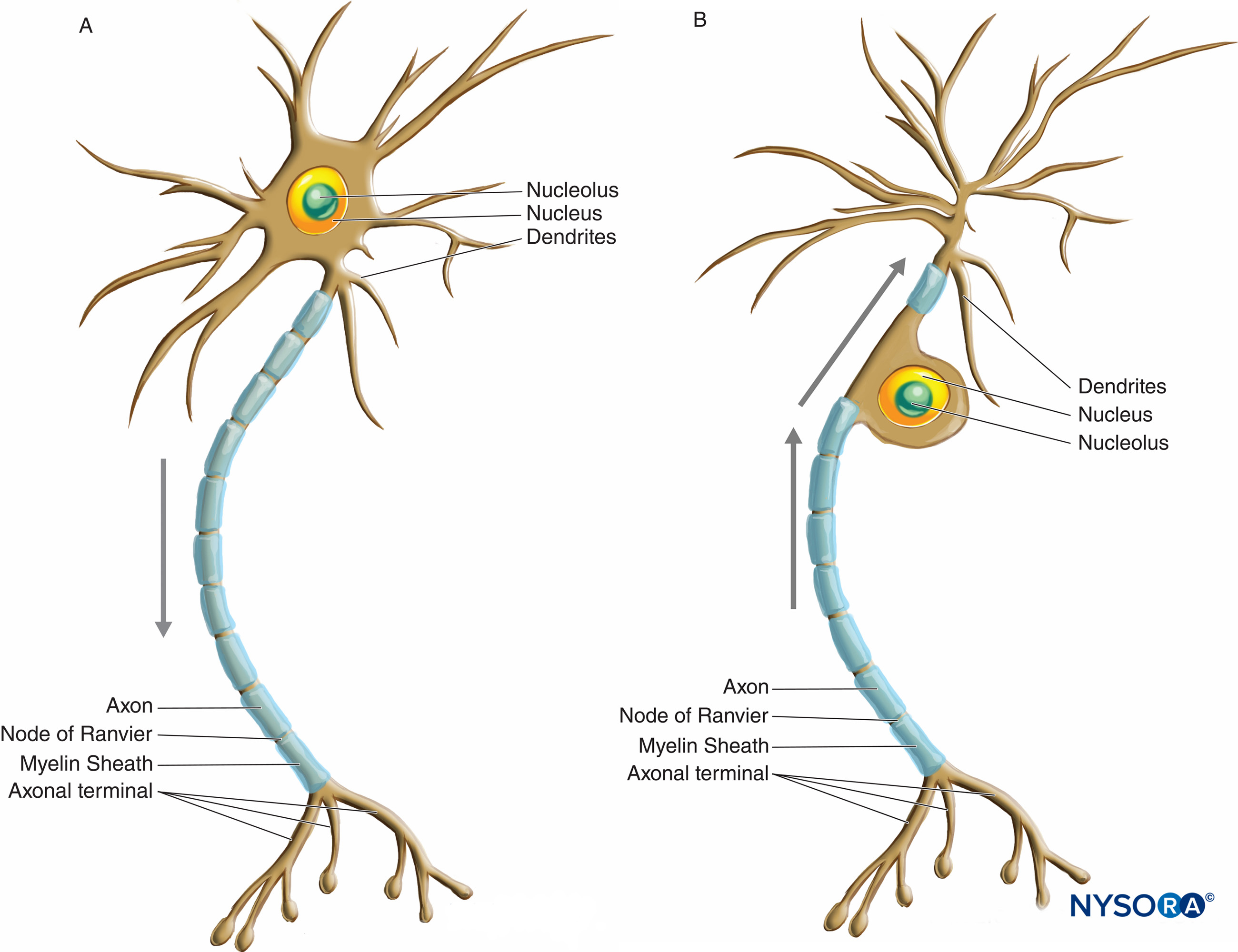
Like other cells, each neuron has a cell body (or soma) that contains a nucleus, smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and other cellular components. Neurons also contain unique structures, illustrated in Figure 16.3 for receiving and sending the electrical signals that make neuronal communication possible.
Color the Neuron and Neuroglial Cells Biology LibreTexts
Like other cells, each neuron has a cell body (or soma) that contains a nucleus, smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and other cellular components. Neurons also contain unique structures, illustrated in Figure 35.3 for receiving and sending the electrical signals that make neuronal communication possible.

Types of neurons. Structure sensory, motor neuron, astrocyte
neuroglia, any of several types of cell that function primarily to support neurons.The term neuroglia means "nerve glue." In 1907 Italian biologist Emilio Lugaro suggested that neuroglial cells exchange substances with the extracellular fluid and in this way exert control on the neuronal environment.It has since been shown that glucose, amino acids, and ions—all of which influence.

Anatomy of the Nervous System Microbiology
Color the Neuron and Neuroglial Cells Oligodendrocytes (purple) Astrocyte (green) Ependymal Cells (orange) Body of Neuron (blue) Myelin sheaths (pink) Capillary (red) Microglial cells (yellow) Nodes or Ranvier and the Axon (brown) What is the function of: 1) Oligodendrocytes ____________________________________________